Understanding the Significance of the Hippocampus
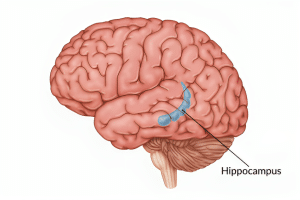
The brain, a complex organ orchestrating myriad bodily functions, houses a crucial region known as the hippocampus. Nestled in the medial temporal lobes of the cerebrum, this region plays a pivotal role in memory, spatial processing, and cognitive functions. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the intricacies of the hippocampus, its vulnerabilities, associated diseases, and the vital nursing responsibilities for patients grappling with hippocampal damage.
The Hippocampus Unveiled:
Situated near the brain’s center, the hippocampus comprises two main components: the hippocampus proper and the dentate gyrus. Its primary association with memory makes it a focal point for researchers and medical professionals seeking to understand the nuances of cognitive processes.
Roles of the Hippocampus:
The hippocampus is not merely a passive recorder of memories; it actively participates in storing long-term memories and rendering them resistant to forgetting. Additionally, its involvement in spatial processing and navigation underscores its multifaceted significance in various cognitive processes, including learning, emotion, and stress.
Vulnerabilities and Impairments:
Despite its importance, the hippocampus is vulnerable to an array of potential damages, ranging from oxygen starvation and inflammation to epilepsy, stroke, head trauma, and the inexorable march of time. Such damages can result in profound impairments, including anterograde amnesia, retrograde amnesia, spatial disorientation, and mood disorders.
Diseases Impacting the Hippocampus:
Several debilitating diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, schizophrenia, and depression, cast a shadow over the hippocampus. Structural and functional changes, such as shrinkage, neuronal loss, altered blood flow, and disrupted neurotransmitter levels, accompany these diseases. These changes significantly hamper the hippocampus’s ability to execute its normal functions, leading to cognitive decline and behavioral problems.
Signs and Symptoms of Hippocampal Damage:
The manifestations of hippocampal damage are diverse and contingent on factors such as the extent, location, and underlying cause of the impairment. Common signs include memory loss, confusion, disorientation, difficulty learning new information, anxiety, depression, and hallucinations. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early intervention and tailored care.
Nursing Responsibilities for Hippocampal Damage Patients:
Providing holistic care to patients with hippocampal damage necessitates a nuanced approach from healthcare professionals. Nursing responsibilities include:
- Comprehensive Assessment: Evaluate cognitive, emotional, and physical status along with ensuring patient safety.
- Stimulation and Support: Engage patients in meaningful activities, reminisce about positive memories, and encourage social interaction to provide emotional support.
- Coping Mechanisms: Assist patients in dealing with memory loss and confusion through cues, reminders, and orientation aids, avoiding confrontation and criticism.
- Patient and Family Education: Educate patients and their families about the nature and effects of hippocampal damage, offering resources and referrals for additional support.
- Collaborative Care: Work closely with neurologists, psychiatrists, psychologists, and therapists to ensure comprehensive care for the patient.
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of the hippocampus and its vulnerabilities is paramount for healthcare professionals striving to provide optimal care to patients grappling with hippocampal damage.
